VAP Group Set to Host Second Edition of Global AI Show in Dubai

In Q2, Nvidia, a world leader in AI and machine learning, held an AI conference. Among the many keynote speakers and panelists at the conference, there was onlly one Web3 representative; Illia Polosukhin, co-founder of NEAR.
At the start of 2024, the hype in Web3 was all about a new Layer 1 protocol that had surpassed both Ethereum and Bitcoin in user activity. The highlight of their growth is their enhancement of the blockchain technology for Web3 and the internet landscape at large
Chads, in this publication of my deep dive series, we turn our attention to the NEAR ecosystem. NEAR is a sharded blockchain that prioritises usability and interoperability. Its main goals are to create better real-world applications for the blockchain and to maximise the blockchain for Artificial Intelligence growth.
This article will explore the foundational principles driving the NEAR ecosystem, its vision for unifying Web3 into a single ecosystem, the user and developer experience on the NEAR protocol, and its plans to seamlessly integrate AI into the blockchain. Additionally, we’ll examine the token at the centre of it all: $NEAR.
What is NEAR aboutLike many other Layer 1 blockchains, NEAR is a proof-of-stake Layer 1 blockchain that gives developers a platform to build decentralised applications.
The core of the NEAR protocol is making Web3 just as conducive for users and developers as Web2 is. One way NEAR plans to do this is the creation of cross-blockchain dApps (which is very much unlike multichain dApps). And NEAR isn’t just working towards making this possible, the ultimate goal is to make it the norm.
While NEAR has made a very impressive rise in DAUs and MAUs, its TVL is still quite low, but the team is not bothered. They claim to be building an environment where users, developers, and projects can thrive before they shift their focus to making money and boosting TVL.
To foster this mission, they have created establishments like the NEAR Academy, NEAR University, and other certified developer programs. With a predominant focus on creation and innovation, NEAR is gradually working its way up to be the best blockchain for users to experience Web3.
NEAR’s Roadmap: ML Program to Web3 ProtocolEarly Days as a Machine Learning Organization (2017–2019)Founding of Near AI
- Founded in 2017 by Alex Skidanov, a former architect and software engineer at memSQL, and Illia Polosukhin, a former Big Data Manager at Google.
- Initially focused on machine learning and fostering global collaboration through open-source contributions, with an emphasis on engaging developers and students.
Challenges Encountered
- Distributing rewards to contributors across various countries presented significant logistical and financial hurdles.
- Existing blockchain solutions were impractical due to high gas fees and insufficient liquidity.
- Traditional financial systems were ineffective for frequent, small-scale global transactions.
Addressing Reward and Liquidity Challenges
- NEAR shifted its focus to decentralized finance (DeFi) to overcome issues with rewarding contributors and managing liquidity.
- The blockchain model emerged as a practical solution for facilitating low-cost, cross-border payments.
Birth of the NEAR Protocol
- Near AI transformed into NEAR, a Layer 1 blockchain protocol.
- The transition was led by NEAR’s core engineering team, known as Pagoda.
- Remarkably, the project secured $500 million in funding even before launching any Web3 products.
Mainnet Launch
- In April 2020, the NEAR Genesis blockchain officially launched.
- 1 billion NEAR tokens were minted and distributed, though token transfers remained locked until October 2020.
Rapid User Growth
- Achieved a remarkable 10x annual increase in users.
- By Q4 2024, the NEAR ecosystem reached 130 million total users.
- Processed over 600 million transactions in Q3 2024 alone.
Milestone Achievements
- Successfully transitioned from a machine learning-focused initiative (Near AI) to a comprehensive blockchain ecosystem.
- Developed a scalable and cost-efficient blockchain protocol designed for global adoption.
- Emerged as a major player in the Web3 and decentralized finance (DeFi) sectors.
- Established itself as a leading Layer 1 blockchain, redefining interoperability and integrating AI advancements into the Web3 landscape.
NEAR’s evolution highlights its adaptability and commitment to solving real-world problems with cutting-edge blockchain technology.
NEAR ProtocolNEAR is a third-generation Layer-1 blockchain designed to prioritize both user and developer accessibility. Leveraging its unique sharding technology, NEAR achieves high throughput and rapid transaction speeds, making it a powerful alternative to first-generation chains like Bitcoin and second-generation Ethereum. With a strong focus on interoperability, NEAR enables seamless communication and asset transfers across different blockchains. According to Illia Polosukhin, one of NEAR’s co-founders, the protocol’s primary goal is to make blockchain technology more accessible, supporting the creation of a diverse ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps).
NEAR’s foundation lies in advanced smart contract capabilities and a highly technical developer community. This has facilitated groundbreaking innovations on the NEAR Genesis chain, such as multichain compatibility through the Rainbow Bridge and a robust BFT consensus system. As with all Layer-1 blockchains, NEAR’s consensus mechanism and operational processes are powered by its native token, $NEAR.
In addition to being a Layer-1 blockchain, NEAR stands out with three distinctive use cases:
- Enhanced dApp Development: NEAR offers a superior environment for decentralized applications, featuring improved multichain interoperability and a developer-friendly infrastructure.
- Optimized Functionality: With its sharding technology, NEAR enables faster NFT transfers and significantly lowers gas fees, providing a more cost-effective and efficient solution.
- Decentralized Governance: NEAR replaces profit-driven corporations with DAOs for managing core blockchain products and services. Decisions are made through consensus voting, ensuring decentralized control across all levels of the chain’s operations.
Now, let’s explore additional features and innovations that make NEAR truly unique:
NightshadeA key feature of NEAR’s operations is its state-of-the-art scalability, which is made possible by its unique sharding system, Nightshade. This custom technology significantly is built to boost the blockchain’s capacity and efficiency in managing high traffic.
Illia highlights a fundamental issue with traditional blockchains: a single computer cannot handle the traffic demands of a large-scale blockchain. While developers can upgrade hardware with larger cores and better specs, there’s still a hard limit to its capacity. NEAR addresses this limitation with an unconventional solution — Nightshade.
Although other blockchains have experimented with sharding, Nightshade stands out due to its innovative approach to handling this process.
What is Sharding?Sharding is a technique that divides large datasets into smaller segments, which are then stored or processed across multiple servers or nodes, referred to as shards.
In the context of blockchains, sharding distributes tasks so that each shard can handle its own transactions independently, guided by smart contracts. This reduces the burden on individual nodes and significantly improves transaction speed and reduces latency.
Nightshade’s Advanced ApproachWhile some blockchains implement basic sharding, NEAR’s Nightshade takes the concept further. Instead of routing the results from shards to a centralised system for verification, Nightshade employs a distributed system managed by four independent computers. This design optimises the process, ensuring greater efficiency and scalability.
A Simplified Breakdown- Becoming a Shard
To qualify as a shard, an account must hold a specified amount of $NEAR tokens. Eligible accounts can volunteer their devices to operate as shards. These shards are then distributed among four computers, each designated to handle specific core processes on the blockchain.
- Instead of every shard reporting to a single computer, they are assigned to specialized computers responsible for distinct tasks, such as transaction processing.
- A single computer might manage over 10 million shards dedicated solely to transactions.
2. Addressing Security Risks
Illia highlights two potential security risks and the measures in place to mitigate them:
Validation Process:
Accounts cannot simply become shards automatically.
- Applicants are subjected to smart contract evaluation and must gain approval through a consensus.
- For efficiency, the smart contract uses a Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus mechanism to validate shards swiftly.
Preventing Targeted Attacks:
A risk exists if users learn which computer their shards are assigned to and attempt to manipulate or take over the process. NEAR counters this by:
- Ensuring users cannot choose which process they shard for.
- Reorganizing shard groupings every 12 hours, leaving no time to coordinate attacks or exploit the system.
These measures reinforce the security and scalability of NEAR’s blockchain while maintaining decentralization.
How Are Shards Distributed?NEAR operates with four specialized computers and manages over 50 million shards and this is how they are distributed:
The validator computer is responsible for handling validation and consensus processes on the smart contract. Since these operations are highly specialized and require minimal computing power, it is assigned approximately 300 shards, the smallest share among all the computers.
The remaining shards are distributed among the high-demand computers, which manage more resource-intensive tasks. These tasks require greater computational power, so the majority of shards are allocated to these computers to handle the increased workload.
NEAR ensures the security of its sharding system through its advanced smart contracts, which are designed to mitigate the risks introduced by sharding while maintaining efficiency and scalability.
Rainbow BridgeThe Rainbow Bridge is NEAR’s key innovation for enabling multichain interoperability. This smart contract is designed to validate inter-chain transfers, but it operates differently from most Web3 bridges. Currently, the Rainbow Bridge is a NEAR<>ETH only network, with plans to extend support to Solana and other blockchains in the future.
The Rainbow Bridge’s functionality is both simple and highly technical. It allows users to transfer their ETH assets to the NEAR blockchain, where they can be used for EVM transactions or interact with decentralized applications (dApps) on both Ethereum and NEAR. This is important because, aside from NEAR’s better traffic handling and faster transaction speeds, the main draw for users is the significantly lower gas fees. On Ethereum, a typical transaction can cost anywhere from $10 to $200, whereas on NEAR, the cost is typically around $0.01. With the Rainbow Bridge, users only need to pay the high Ethereum gas fees once to transfer their assets, after which they can enjoy much cheaper and faster transactions within the same EVM ecosystem on NEAR.
AuroraAurora is the final piece in NEAR’s innovative trinity. It is an EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) designed to understand and execute smart contracts created for the Ethereum blockchain. This is a game-changer for developers, as NEAR’s simpler programming language and faster validation times make it an ideal environment for building decentralized applications (dApps) and pushing them to the mainstream more efficiently.
Aurora replicates the ERC-20 environment found on Ethereum, allowing dApps built on NEAR to be fully compatible with ERC-20 blockchains. For developers, this means they can create applications on NEAR and easily transfer them to the Ethereum blockchain without modifications. Building on Aurora ensures that dApps are ready to run smoothly on Ethereum, giving developers the flexibility to work on both networks with ease.
NEAR’s ecosystem is designed to encourage high retention rates among both developers and users. Let’s explore how it serves these two key groups.
NEAR’s Developer EcosystemThe first standout feature of NEAR’s developer ecosystem is the seamless migration process. Developers who have been working on ERC-20 blockchains don’t need to rebuild their apps when moving to the NEAR blockchain. With the help of Aurora technology, they can simply copy their work to NEAR and continue development without disruption.
This migration also allows developers to offer the same functionality of their dApps, but with the added benefits of lower fees and faster speeds. Additionally, NEAR makes the transition easy for developers coming from Web2, supporting familiar programming languages such as Rust, JavaScript, and Solidity on Aurora.
NEAR’s User EcosystemSince its inception, NEAR has seen significant growth in its user base. To highlight this progress, let’s examine some key figures:
- In Q3, the ecosystem added 30 million new users, bringing the total user count to 130 million. During the same period, users conducted around 600 million transactions on-chain, averaging 6.3 million transactions daily.
- The blockchain saw a remarkable rise in daily active users (DAUs), with 3.1 million DAUs in Q3, up from 1.6 million in Q1. Furthermore, monthly active users (MAUs) reached an impressive 22.1 million in Q3, compared to 13 million in Q2.
- In terms of retention, only 0.28 million of the 3.1 million DAUs in Q3 were new wallet holders, while the remaining 2.8 million users were existing ones who became more active due to platform upgrades and new innovations.
How does NEAR achieve this? The answer is quite simple; Accessibility.
The ecosystem is designed to be accessible for Web2 normies to transition, while also enabling seamless interaction with other Gen1 and Gen2 blockchains within a single ecosystem.
One of the key user-centric features of NEAR is its onboarding process. It begins by integrating Web2 apps that reward users with redeemable tokens, with Sweatcoin being a prime example. NEAR then provides financial backing for these tokens on the blockchain, giving them real utility. Users of these apps can redeem their tokens by making purchases from businesses that accept them. Thanks to NEAR, these transactions happen on-chain, but users don’t need a NEAR wallet. Instead, the process is facilitated by a technology called chain signatures, allowing on-chain activities without the need for a wallet.
Chain signatures allow users to access features on the ecosystem without having gas tokens. Transactions like this are called meta transactions.
Following this, the app can prompt users to create a proper wallet to unlock additional in-app features. By offering tangible value through functional utilities, NEAR ensures a high conversion rate and successful onboarding of active users.
Another key feature is on-chain accessibility. With a NEAR wallet, users no longer need multiple wallets, as the network continues to expand. Thanks to technologies like Aurora and the Rainbow Bridge, users gain access to a broad segment of the Web3 ecosystem directly from the NEAR Genesis blockchain.
As Illia explains, simply asking users to download a wallet like MetaMask or any other wallet isn’t enough. You must provide real value that naturally guides users into the Web3 space. And so far, this philosophy has been working very well for NEAR.
NEAR’s Artificial IntelligenceA major highlight of NEAR’s development, especially during its presentation at Nvidia’s convention this year, has been its integration of AI into Web3. While addressing challenges within Web3, NEAR introduces AI with a new functionality on the blockchain, while also aiming to resolve AI’s limitations using blockchain technology.
The integration of AI into the blockchain serves two main functions: Work and Governance.
AI in Work:By incorporating AI into Web3, AI can now leverage the blockchain’s public ledger as a valuable information source. This allows AI to provide insights and solutions using data from both Web2 and Web3, making it a more informed resource for users in the Web3 ecosystem. Additionally, AI can manage large-scale data analytics related to financial flows, operational performance, and financial states, helping Web3 companies scale while ensuring their data remains secure on the blockchain. AI can also assist with work verification and task delegation by analyzing individual behaviour and distributing tasks based on people’s strengths.
AI in GovernanceWhile DAOs are inherently decentralised, NEAR Protocol recognises the need for an objective coordinator to organise information and provide context to each individual contributor. The AI analyses each contributor to know their strengths and how much context they would need to make a well-informed decision within the DAO.
On the other hand, blockchain technology can enhance the integrity and transparency of AI. By allowing users to track the origin and history of information, blockchain prevents the spread of misinformation. Also, centralised AI regulation is facing challenges due to the rapid pace of development and the global nature of AI research. Blockchain and smart contracts can provide a more effective regulatory framework. By automating the enforcement of AI guidelines and standards, smart contracts can ensure compliance and accountability on a global scale.
NEAR’s DeFi Ecosystem and TokenomicsFirst, let’s look at the numbers:
- $NEAR has a relatively low TVL (Total Value Locked) compared to other Layer1 blockchains, but it is showing solid growth. At the start of 2024, $NEAR’s TVL was at $100 million, at the end of Q3, it had increased to $250 million.
- NEAR introduced a meme token launchpad; meme.cooking. Within the first two hours of operation, meme.cooking reached a TVL of $54,000. Thanks to bullish memes with great community support like BLACKDRAGON at $8.1 million MC, and PURGE at $20 million MC.
- $325 million in on-chain assets have been allocated for liquid staking.
An interesting point to note is that NEAR consistently held its value throughout the bear market even with a 5% annual inflation rate, NEAR managed to do this through two major practices.
They two major practices are;
- Burning: Gas fees on the NEAR network are split two ways. 70% goes to the developers as revenue, while the other 30% is burned to maintain scarcity.
- Token Locking: Early investors of the project have their tokens locked, with limited periodic access to them. This prevents top holders from causing instability in the token valuation.
In terms of supply, 1 billion $NEAR tokens were minted at launch, and currently, only 754 million remain, without affecting the token’s valuation.
For functionality, $NEAR serves as a utility token for transactions on the NEAR chain and others. It’s also used for governance, with a shard required to hold at least 20,000 $NEAR to be part of the Nightshade network.
NEAR vs Cardano vs Sui vs SolanaTo understand the growth of NEAR and its effect on the Web3 space, let us place it side-by-side with other third generation blockchains.
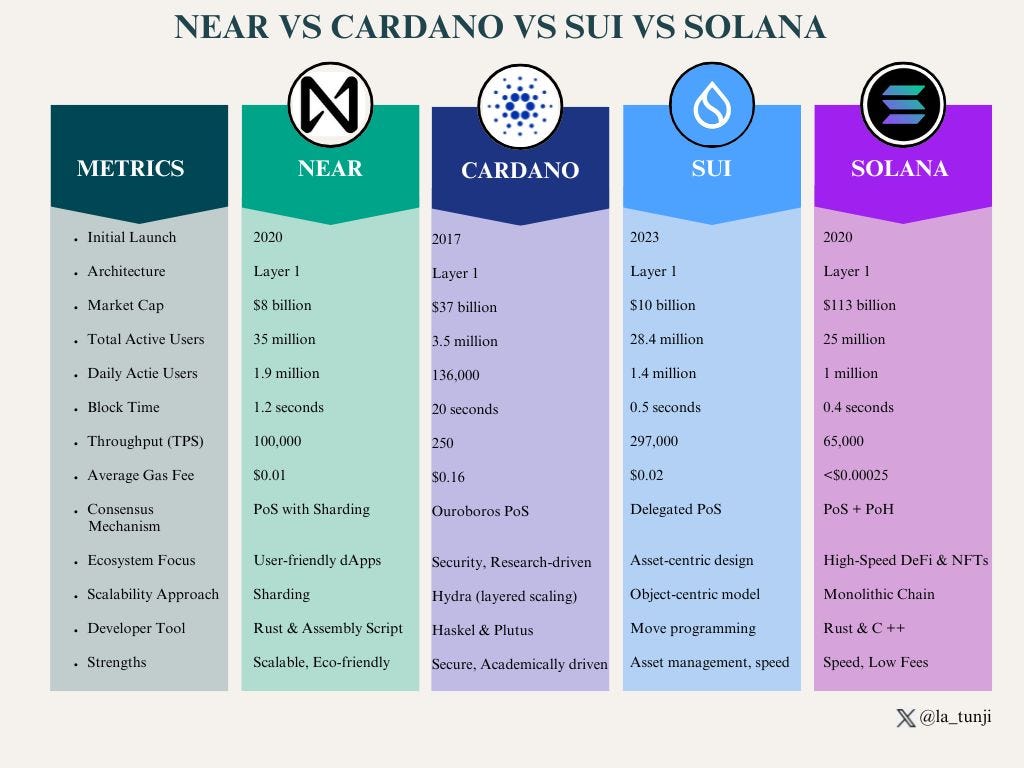 Wrap-up
Wrap-upWhat NEAR aims to create is a world of chain abstraction. A world where user can access Web3 without the limitations that come from using different blockchains. Their goal is to make Web3 as seamless as Web2; in Web2, when you access a database, you don’t need to know whether the server is local, international, or owned by Google, because databases are designed to function as a unified network. Imagine a Web3 where users don’t have to worry about which chains they are using or manage multiple accounts for inter-chain transactions.
According to Illia Polosukhin, NEAR is not building for just the NEAR ecosystem, not even just for Web3, but for the entire online population. They have a vision to onboard ! billion internet users to Web3 with an average of 100 million MAUs on chain.
However, achieving chain abstraction is a complex challenge, which is why many projects shy away from it. It requires time and effort, and I appreciate projects like NEAR that are committed to pushing the boundaries for the growth of Web3.
Deep Dive Into The NEAR Ecosystem was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
