Discover the Power of Asset Tokenization
AI agents are revolutionizing customer service by enhancing efficiency and personalization. These advanced systems leverage machine learning and natural language processing to handle a range of tasks, from answering routine inquiries to resolving complex issues. Their capabilities include 24/7 availability, instant response times, and the ability to process vast amounts of data to deliver tailored customer interactions. Practical applications of AI agents extend to automating repetitive tasks, improving response accuracy, and providing insights into customer behavior.
 Fig: AI Agents in Customer Service
Fig: AI Agents in Customer ServiceThe benefits are significant, including reduced operational costs, increased customer satisfaction, and the ability to scale support efforts effortlessly. Implementing AI agents involves selecting the right technology platform, integrating it with existing systems, and continuously monitoring and refining its performance to ensure it meets business objectives and customer expectations. As businesses increasingly adopt AI solutions, understanding how to effectively deploy these tools is crucial for gaining a competitive edge and delivering exceptional customer service.
Table of ContentUnderstanding AI Agents in Customer ServiceHow do AI Agents Work in Customer Service?
Benefits of AI Agents in Customer Service
Types of AI Agents in Customer Service
Why Does the Customer Service Sector Need AI Agents?
Role of AI Agents in Customer Service Process
Use cases of AI Agents in Customer Service
Building LLM-based AI Agents for Customer Service: A Step-By-Step Guide
The Future of AI in Customer Service
ConclusionUnderstanding AI Agents in Customer Service
Understanding AI agents in customer service involves recognizing their transformative potential and operational dynamics. These sophisticated systems utilize artificial intelligence to manage and enhance customer interactions through capabilities such as natural language processing, machine learning, and automation. AI agents in customer service can perform a variety of functions, including handling customer inquiries, processing transactions, and providing personalized recommendations. Their ability to operate continuously without fatigue ensures that customers receive prompt and consistent support.
AI agents also offer significant benefits such as cost reduction, improved efficiency, and valuable data insights that help businesses refine their strategies and enhance service quality. Implementing AI agents requires careful planning, including selecting the right technology, integrating it with existing systems, and training the system to understand and respond effectively to customer needs. As technology evolves, AI agents will become increasingly sophisticated, enabling businesses to deliver superior customer experiences and stay ahead in a competitive market. Understanding and leveraging these tools effectively is key to optimizing customer service and achieving long-term success.
How do AI Agents Work in Customer Service?AI agents, or chatbots, have become increasingly prevalent in customer service. Here’s a breakdown of how they work and their benefits:
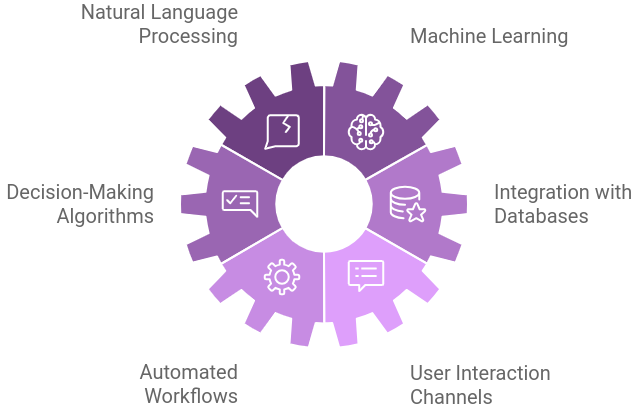 1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)AI agents use NLP to understand and process human language. This involves:
- Speech Recognition: Converting spoken language into text.
- Text Analysis: Parsing and understanding written text. This includes recognizing intent and extracting relevant information from user inputs.
AI agents are often powered by machine learning algorithms that allow them to:
- Learn from Interactions: They can improve over time by learning from past interactions and user feedback.
- Predict User Needs: By analyzing historical data, AI agents can predict and preemptively address customer needs.
AI agents use decision-making algorithms to:
- Determine Responses: Based on the analysis of the user’s query, they generate appropriate responses or take actions.
- Provide Contextual Help: They can keep track of the conversation context to provide relevant assistance.
AI agents are integrated with databases to:
- Access Information: Retrieve information about products, services, or user accounts.
- Update Records: Make changes to user profiles or other data based on interactions.
AI agents can automate various tasks, such as:
- Handling Routine Inquiries: Answer frequently asked questions, process orders, or provide account information.
- Escalating Issues: Recognize when an issue needs human intervention and escalate it accordingly.
AI agents can interact with users across multiple channels, including:
- Websites: Via embedded chat widgets.
- Mobile Apps: Through integrated chat features.
- Social Media: By interacting on platforms like Facebook Messenger or Twitter.
AI agents are continuously evolving, with advancements in AI and NLP making them increasingly sophisticated and capable of handling complex customer service tasks.
Benefits of AI Agents in Customer ServiceAI agents offer several significant benefits in customer service, enhancing both the customer experience and operational efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at these benefits:
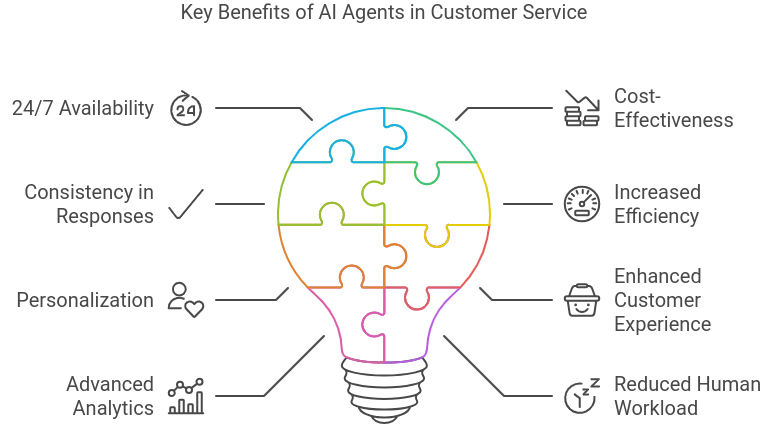 1. 24/7 Availability
1. 24/7 Availability- Around-the-Clock Support: AI agents can operate continuously, assisting at any time, which is especially valuable for global businesses across different time zones.
- Reduced Operational Costs: By automating routine tasks and inquiries, AI agents reduce the need for a large customer service team, leading to lower labor costs.
- Scalability: Easily handles increasing volumes of queries without a proportional increase in costs.
- Standardized Information: Provides uniform answers to common questions, ensuring consistency and reducing the likelihood of misinformation.
- Error Reduction: Minimizes human errors in responding to customer inquiries.
- Faster Response Times: Processes and responds to queries more quickly than human agents, leading to shorter wait times for customers.
- Handling Volume: Manages a high volume of interactions simultaneously, which helps in reducing backlogs and improving service efficiency.
- Tailored Interactions: Leverages data and past interactions to provide personalized responses and recommendations, enhancing the customer experience.
- User Profiling: Uses CRM data to customize interactions based on user history and preferences.
- Immediate Assistance: Provides instant answers to customer questions, improving satisfaction and engagement.
- Multichannel Support: Offers support across various channels (e.g., chat, email, voice) to meet customers where they are most comfortable.
- Data Insights: Gathers and analyzes data from customer interactions to identify trends, common issues, and areas for improvement.
- Performance Tracking: Monitors key metrics such as response accuracy, resolution times, and customer satisfaction.
- Automated Routine Tasks: Handles repetitive and low-complexity tasks, allowing human agents to focus on more complex and nuanced issues.
- Error Handling: Takes care of common queries and straightforward issues, freeing up human agents for higher-value interactions.
- Adaptability: Easily scales up or down based on demand, making it ideal for handling seasonal peaks or rapid growth.
- Flexible Integration: Can be integrated with various systems and platforms to extend its functionality and adapt to different business needs.
- Learning Capabilities: Continuously learns from interactions and feedback to improve accuracy and performance over time.
- Feedback Incorporation: Uses user feedback to refine algorithms and enhance the quality of responses.
- Consistent Quality: Ensures high-quality responses by adhering to predefined guidelines and standards.
- Error Prevention: Reduces the likelihood of human error in customer interactions.
Overall, AI agents significantly enhance customer service by providing quick, accurate, and personalized support, while also contributing to cost savings and operational efficiency.
Types of AI Agents in Customer ServiceIn customer service, AI agents come in various forms, each tailored to address specific needs and functions. Here are the main types of AI agents used in customer service:
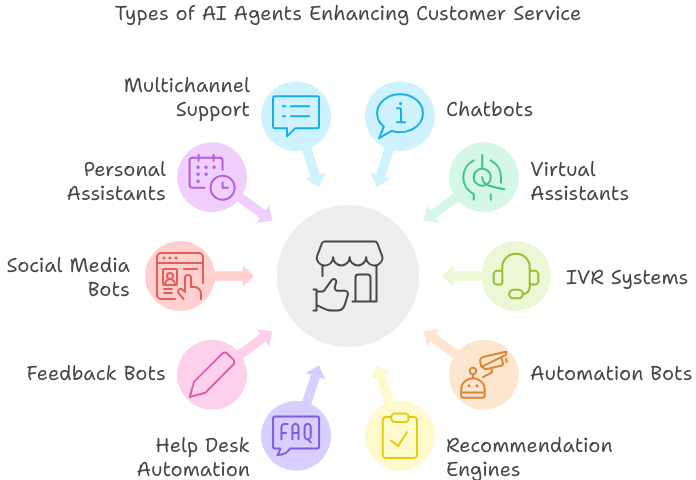 1. Chatbots
1. Chatbots- Rule-Based Chatbots: Operate based on a set of predefined rules and decision trees. They follow specific instructions and provide answers to straightforward queries.
- AI-Powered Chatbots: Utilize natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand and respond to more complex queries. They can learn from interactions and improve over time.
- Voice Assistants: Engage with customers through voice commands and responses. They are commonly used in phone support or integrated into voice-activated devices (e.g., Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant).
- Text-Based Assistants: Operate through text-based communication channels such as chat windows or messaging apps, providing similar functionalities to voice assistants but through written interactions.
- Automated IVR: Uses pre-recorded voice prompts to guide users through a series of options. It helps in routing calls to the appropriate department or providing information without human intervention.
- AI-Enhanced IVR: Incorporates AI to understand natural language and provide more sophisticated interactions, such as answering complex queries or recognizing customer intent.
- Support Bots: Handle specific tasks such as ticketing, order processing, or account management. They automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human agents for more complex issues.
- Resolution Bots: Assist in resolving customer issues by providing solutions based on the context of the inquiry, often integrating with knowledge bases or FAQs.
- Product Recommendation Bots: Use algorithms to suggest products or services based on user preferences, behavior, or past interactions.
- Content Recommendation Bots: Provide personalized content recommendations, such as articles or offers, tailored to the user’s interests and behavior.
- Knowledge Base Integration: Accesses and retrieves information from a knowledge base to answer customer queries or provide troubleshooting assistance.
- Ticketing System Integration: Creates, updates, and manages support tickets, often integrating with customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
- Survey Bots: Conduct customer satisfaction surveys or collect feedback on service quality. They automate the process of gathering and analyzing customer opinions.
- Feedback Bots: Solicit feedback during or after interactions to gauge customer satisfaction and identify areas for improvement.
- Social Listening Bots: Monitor social media channels for mentions of the brand, sentiment, or emerging trends. They can alert human agents to potential issues or opportunities.
- Social Engagement Bots: Interact with customers on social media platforms, responding to comments, messages, and mentions to maintain engagement and address concerns.
- Contextual Personal Assistants: Provide personalized assistance based on user history, preferences, and real-time context, offering a more tailored and relevant experience.
- Proactive Personal Assistants: Anticipate user needs and proactively offer assistance or recommendations based on predictive analytics.
- Omnichannel Bots: Provide seamless support across various communication channels, such as chat, email, social media, and SMS. They ensure consistent and unified interactions regardless of the channel.
Each type of AI agent serves a specific role in enhancing customer service, from handling routine inquiries to providing personalized recommendations and feedback. The choice of AI agent depends on the business needs, customer expectations, and the complexity of interactions.
Why Does the Customer Service Sector Need AI Agents?The customer service sector benefits significantly from AI agents due to several compelling reasons. Here’s why AI agents are becoming essential in customer service:
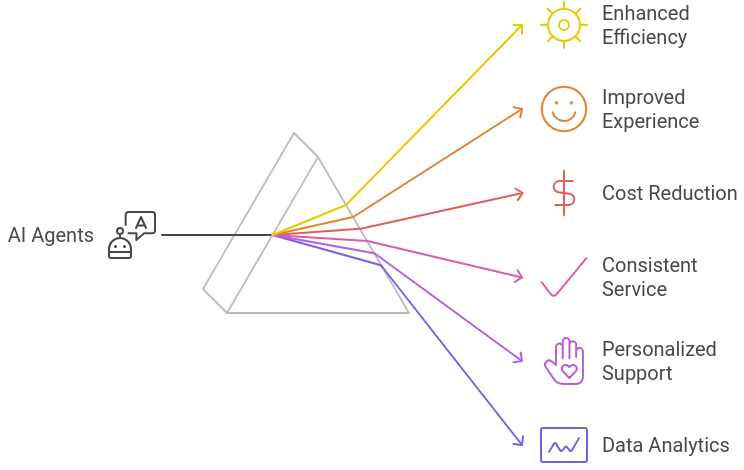 1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity- Automating Routine Tasks: AI agents handle repetitive tasks such as answering frequently asked questions, processing simple requests, and managing basic queries. This frees up human agents to focus on more complex and nuanced issues.
- Handling High Volumes: AI agents can manage a large number of interactions simultaneously, which helps in scaling customer service operations without a proportional increase in resources.
- Faster Response Times: AI agents provide immediate responses, reducing wait times and improving the overall customer experience.
- 24/7 Availability: They offer round-the-clock support, ensuring that customers can get assistance at any time, regardless of time zones or business hours.
- Lower Operational Costs: By automating routine interactions, businesses can reduce the need for a large customer service team, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Scalability: AI agents can easily scale up to handle increased demand without a corresponding increase in costs, making them a cost-effective solution.
- Uniform Responses: AI agents provide consistent answers based on predefined guidelines and knowledge bases, ensuring that customers receive accurate and reliable information.
- Error Reduction: They minimize human errors and inconsistencies in responses, leading to more dependable service.
- Tailored Interactions: AI agents can use data from past interactions to personalize responses and recommendations, enhancing the relevance of their assistance.
- Behavior Analysis: They analyze user behavior and preferences to offer customized support and suggestions, improving customer satisfaction.
- Insight Generation: AI agents collect and analyze data from customer interactions to identify trends, common issues, and areas for improvement.
- Performance Tracking: They track key metrics such as response accuracy and customer satisfaction, providing valuable insights for optimizing service operations.
- Omnichannel Presence: AI agents can interact with customers across various channels, including chat, email, social media, and voice, ensuring a seamless and integrated customer experience.
- Unified Service: They maintain consistent support across different platforms, providing a cohesive experience for users.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI agents can anticipate customer needs based on historical data and behavior, offering proactive solutions and recommendations.
- Issue Prevention: They can identify potential issues before they escalate, helping to prevent customer dissatisfaction.
- Continuous Learning: AI agents learn from interactions and feedback to improve their performance and accuracy over time.
- Feedback Collection: They gather customer feedback efficiently, helping businesses understand customer sentiment and make data-driven improvements.
- Support for Human Agents: AI agents assist human agents by handling routine tasks and providing information, allowing human agents to focus on more complex and high-value interactions.
- Augmented Decision-Making: They provide human agents with real-time information and insights, supporting better decision-making and problem-solving.
AI agents address key challenges in customer service by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, improving consistency, and providing personalized and proactive support. Their integration into customer service operations helps businesses meet increasing customer expectations and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
Role of AI Agents in Customer Service ProcessAI agents play a transformative role in the customer service process by enhancing various aspects of interactions between customers and businesses. Here’s a detailed look at their roles throughout the customer service process:
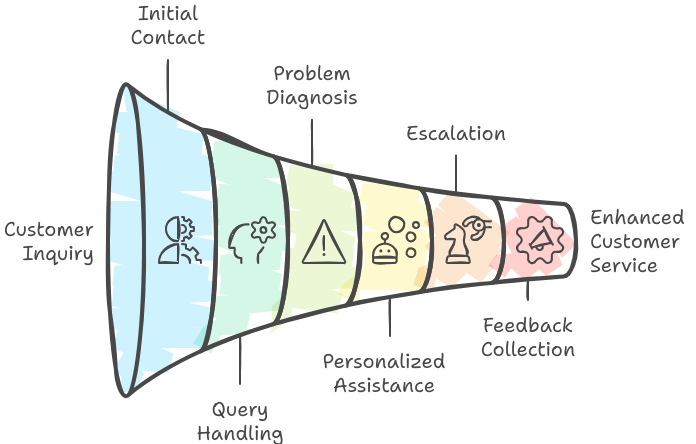 1. Initial Contact and Query Handling
1. Initial Contact and Query Handling- Instant Response: AI agents provide immediate responses to customer inquiries, reducing wait times and ensuring prompt attention.
- Query Categorization: They classify and prioritize queries based on their content, directing them to appropriate resources or departments.
- Knowledge Base Access: AI agents retrieve information from knowledge bases or FAQs to answer questions about products, services, or policies.
- Contextual Understanding: They understand the context of the inquiry to provide relevant and accurate information.
- Issue Identification: AI agents analyze customer inputs to identify the nature of the problem or request.
- Automated Resolution: For straightforward issues, they provide solutions or guidance based on predefined rules and information.
- Tailored Responses: AI agents use customer data and interaction history to deliver personalized responses and recommendations.
- Behavioral Analysis: They analyze user behavior to anticipate needs and offer relevant suggestions or solutions.
- Complex Issue Handling: When encountering complex or unresolved issues, AI agents escalate the query to human agents with relevant context and information.
- Seamless Transition: They ensure a smooth handoff by providing human agents with a detailed history of the interaction and any actions taken.
- Feedback Collection: AI agents solicit feedback from customers on their experience and satisfaction, often through surveys or follow-up questions.
- Follow-Up Actions: Based on feedback, they may initiate follow-up actions or communications to address any remaining issues or concerns.
- Interaction Tracking: AI agents log and track interactions, gathering data on customer inquiries, responses, and outcomes.
- Analytics and Insights: They analyze collected data to identify trends, common issues, and areas for improvement, providing valuable insights for business optimization.
- Predictive Assistance: AI agents use predictive analytics to anticipate customer needs and proactively offer assistance or solutions.
- Engagement Triggers: They initiate interactions based on user behavior, such as offering help when a user seems stuck or providing recommendations based on previous interactions.
- Consistent Experience: AI agents provide support across various channels, including chat, email, social media, and voice, ensuring a consistent and unified customer experience.
- Channel Integration: They manage interactions across different platforms, maintaining context and continuity in customer service.
- Workflow Automation: AI agents automate repetitive tasks and processes, streamlining workflows and reducing the workload on human agents.
- Resource Allocation: By handling routine inquiries, they allow human agents to focus on more complex and high-value tasks, optimizing resource allocation.
- Agent Support: AI agents assist human agents by providing real-time information, suggestions, and best practices during interactions.
- Continuous Learning: They learn from interactions and feedback to improve their performance and accuracy, adapting to new types of queries and evolving customer expectations.
- Cost Reduction: By automating many aspects of customer service, AI agents reduce the need for a large customer support team, leading to significant cost savings.
- Scalable Solutions: They offer scalable solutions that can handle varying volumes of customer interactions without proportional increases in costs.
AI agents enhance the customer service process by improving response times, personalizing interactions, handling routine tasks, and providing valuable insights. Their integration into customer service operations leads to more efficient, effective, and satisfying customer experiences.
Use cases of AI Agents in Customer ServiceAI agents are employed across various use cases in customer service to streamline processes, enhance user experiences, and improve efficiency. Here’s a detailed overview of some common and impactful use cases:
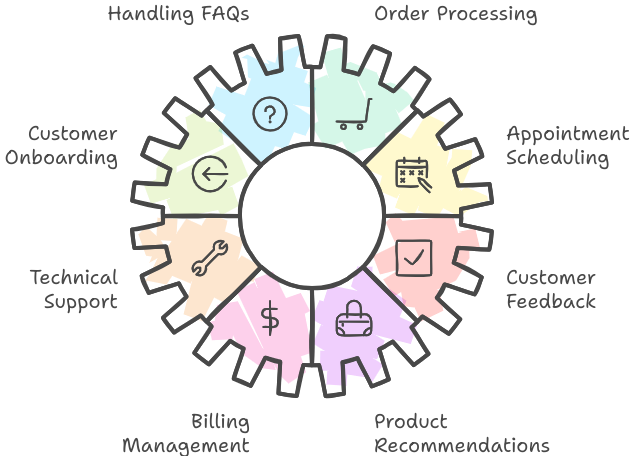 1. Handling Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Handling Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)- Automated Responses: AI agents provide instant answers to common questions about products, services, policies, and procedures.
- Knowledge Base Access: They pull information from a knowledge base to ensure accurate and consistent responses.
- Order Placement: Assist customers in placing orders, selecting products, and managing cart contents through conversational interfaces.
- Order Tracking: Provide real-time updates on order status, shipping information, and delivery estimates.
- Guided Setup: Assist new customers with the setup process, including account creation, initial configuration, and product setup.
- Educational Content: Provide onboarding tutorials, FAQs, and helpful tips to ensure a smooth start for new users.
- Booking Appointments: Help customers schedule appointments, book services, or reserve time slots through chat or voice interfaces.
- Reminder Notifications: Send reminders and confirmations for upcoming appointments, reducing no-show rates.
- Issue Diagnosis: Assist in diagnosing technical issues based on user symptoms and error messages.
- Troubleshooting Guides: Provide step-by-step troubleshooting instructions to resolve common technical problems.
- Feedback Collection: Solicit feedback from customers on their service experience, product satisfaction, or other aspects.
- Survey Administration: Conduct surveys to gather insights and opinions on various topics, helping to improve services.
- Billing Inquiries: Address questions related to billing, payments, invoices, and account charges.
- Account Updates: Assist in updating account details, such as contact information, payment methods, or subscription plans.
- Personalized Suggestions: Recommend products or services based on customer preferences, browsing history, or purchase behavior.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Suggest complementary or upgraded products to enhance the customer’s experience.
- Complaint Logging: Record customer complaints and issues, ensuring they are routed to the appropriate department or human agent.
- Resolution Assistance: Provide information on the complaint resolution process and status updates.
- Unified Communication: Offer support across multiple channels, including chat, email, social media, and voice, providing a seamless experience.
- Channel Integration: Maintain context and continuity of interactions across different communication platforms.
- Behavioral Triggers: Initiate interactions based on customer behavior, such as offering assistance when a user seems stuck or providing recommendations based on recent activity.
- Alerts and Notifications: Send proactive notifications about account updates, new features, or relevant promotions.
- Booking and Reservations: Assist with booking flights, hotels, and other travel services, including modifications and cancellations.
- Travel Information: Provide information on travel itineraries, local attractions, and travel advisories.
- Claims Filing: Guide customers through the process of filing insurance claims, and collecting necessary information and documentation.
- Claim Status: Provide updates on the status of claims and the next steps in the processing pipeline.
- Product Inquiries: Answer questions about product specifications, availability, and pricing.
- Order Support: Handle issues related to returns, exchanges, and refunds.
- Appointment Scheduling: Help patients schedule medical appointments and manage their health records.
- Medical Information: Provide information on symptoms, treatments, and general health advice (though not a substitute for professional medical advice).
- Account Inquiries: Assist with inquiries related to banking accounts, transactions, and financial services.
- Fraud Detection: Monitor for unusual activity and alert customers or take preventive actions.
These use cases illustrate the versatility of AI agents in addressing a wide range of customer service needs. By automating routine tasks, providing personalized support, and enhancing operational efficiency, AI agents contribute to a more effective and satisfying customer service experience.
Building LLM-based AI Agents for Customer Service: A Step-By-Step GuideBuilding Large Language Model (LLM)--based AI agents for customer service involves several steps, from initial planning to deployment and ongoing maintenance. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
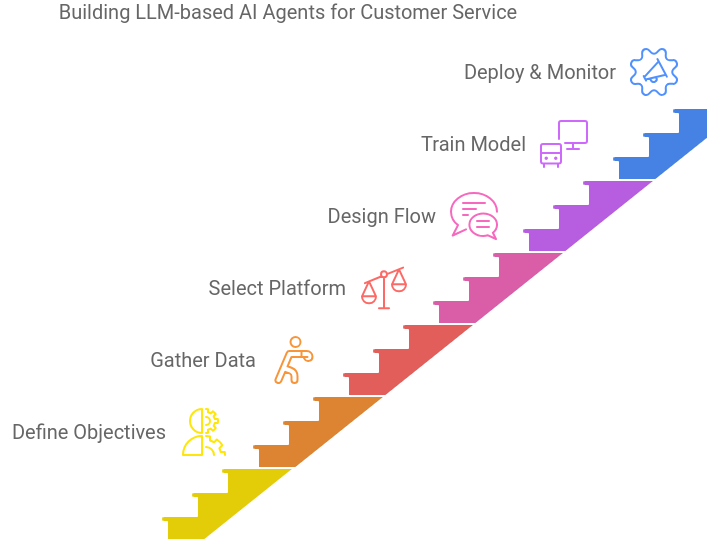 1. Define Objectives and Scope
1. Define Objectives and Scope- Identify Goals: Determine what you want the AI agent to achieve (e.g., handling FAQs, processing orders, providing technical support).
- Scope of Functionality: Define the specific tasks and interactions the AI agent will handle. This helps in tailoring the model’s capabilities to meet your needs.
- Data Collection: Collect relevant data for training, such as customer service logs, FAQs, and interaction transcripts. Ensure the data covers a broad range of scenarios and queries.
- Data Cleaning: Clean the data to remove inconsistencies, errors, and irrelevant information. This step is crucial for training an effective and accurate model.
- Data Annotation: Annotate the data to label different types of queries, intents, and responses, helping the model learn the relationships between them.
- Choose a Model: Select a suitable Large Language Model (e.g., GPT-4, GPT-5) based on your requirements for complexity, performance, and cost.
- Platform Integration: Decide whether to use a cloud-based LLM service (e.g., OpenAI, Azure AI) or a locally hosted model, considering factors like scalability and data security.
- User Intent Identification: Define the intents (user goals) that the AI agent should recognize and handle.
- Dialogue Management: Design the flow of conversations, including how the AI agent should handle different intents, follow-up questions, and contextual transitions.
- Response Generation: Develop templates or guidelines for generating responses, ensuring they are accurate, relevant, and aligned with your brand’s tone and style.
- Fine-Tuning: Fine-tune the LLM using your prepared dataset to adapt it to your specific use case. This process involves adjusting the model’s parameters to improve the performance of your data.
- Evaluation: Test the model’s performance using validation datasets to ensure it meets your accuracy and response quality standards.
- System Integration: Integrate the AI agent with existing customer service systems such as CRM platforms, ticketing systems, and communication channels (e.g., chat, email).
- APIs and Webhooks: Set up APIs and webhooks to facilitate interactions between the AI agent and other systems, enabling functionalities like real-time data retrieval and updates.
- Chat Interface: Design and develop the user interface through which customers will interact with the AI agent (e.g., website chat widget, mobile app).
- Voice Interface: If applicable, integrate voice recognition and synthesis capabilities for voice-based interactions.
- Pilot Testing: Conduct pilot tests with a limited user group to identify any issues or areas for improvement.
- User Feedback: Collect feedback from users to assess the AI agent’s performance, usability, and effectiveness.
- Iterative Refinement: Make necessary adjustments based on test results and user feedback to enhance the AI agent’s performance and user experience.
- Deployment: Roll out the AI agent to your customer service channels. Ensure that it is fully operational and integrated with all relevant systems.
- Monitoring: Continuously monitor the AI agent’s performance, including response accuracy, user satisfaction, and interaction volume.
- Error Handling: Set up mechanisms for detecting and addressing issues or errors that may arise during live interactions.
- Regular Updates: Update the model periodically with new data to keep it relevant and effective. Incorporate changes based on emerging trends and customer feedback.
- Performance Metrics: Track key performance metrics such as response time, resolution rate, and customer satisfaction to measure and improve the AI agent’s performance.
- User Training: Provide training or resources for human agents to work effectively with the AI agent, including how to handle escalations and leverage AI-generated insights.
- Data Privacy: Ensure that the AI agent complies with data protection regulations and best practices for handling sensitive customer information.
- Security Measures: Implement robust security measures to protect the AI agent and customer data from unauthorized access and breaches.
By following these steps, you can build a robust and effective LLM-based AI agent for customer service that enhances efficiency, improves customer satisfaction, and supports your overall service goals.
The Future of AI in Customer ServiceThe future of AI in customer service promises remarkable advancements, driven by continuous improvements in technology and evolving consumer expectations. AI is set to become even more integral, with developments in natural language processing and machine learning enhancing the ability of AI agents to understand and respond to customer queries with greater accuracy and empathy. Predictive analytics will enable AI systems to anticipate customer needs and offer proactive solutions, further personalizing the service experience.
Integration with other technologies, such as chatbots and virtual assistants, will streamline interactions and provide seamless, multi-channel support. As AI evolves, its role will expand to include more complex problem-solving and decision-making capabilities, reducing the need for human intervention while improving overall efficiency. Businesses will need to adapt to these changes by investing in advanced AI solutions and focusing on continuous training and optimization. Embracing these future trends will be crucial for companies aiming to deliver exceptional customer experiences and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital landscape.
ConclusionIn conclusion, AI agents are a game-changer in customer service, offering unmatched efficiency and personalization. Their capabilities to operate around the clock, handle diverse customer inquiries, and analyze data for improved interactions make them indispensable in modern customer support. By automating repetitive tasks and providing valuable insights, AI agents not only reduce operational costs but also enhance customer satisfaction and engagement.
To maximize the benefits of AI in customer service, businesses must carefully select appropriate technology, ensure seamless integration with current systems, and continuously monitor performance to adapt to evolving customer needs. As AI technology advances, its role in customer service will become even more integral, making it essential for businesses to embrace these tools to stay competitive. Embracing AI agents can lead to more efficient operations, better customer experiences, and a stronger market position, highlighting the importance of strategic implementation and ongoing optimization.
The Role of AI Agents in Customer Service: Capabilities, Practical Uses, Benefits, and How to… was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
