What Are the Key Benefits of Using AI in Drones?
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, artificial intelligence (AI) stands out as a game-changing force across multiple industries. Startups, in particular, have a unique opportunity to harness AI’s capabilities to create innovative solutions that address real-world problems and enhance customer experiences. As businesses increasingly adopt AI-driven strategies, the demand for intelligent applications is soaring, paving the way for entrepreneurs to explore new and profitable avenues. From improving operational efficiencies to delivering personalized services, AI is transforming how companies operate and engage with their customers.
As we delve into the top AI business ideas for startups, it becomes evident that the potential for growth and innovation is vast. This blog will highlight various AI-driven ventures, ranging from health tech to e-commerce and beyond, each with its unique market potential and benefits. Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur or an established business owner looking to pivot, understanding these AI business ideas can empower you to leverage technology effectively, stay ahead of the competition, and create a sustainable impact in the ever-changing market landscape.
1. AI-Powered ChatbotsOverview
AI-powered chatbots are advanced software applications designed to simulate human conversation through voice or text interactions. These chatbots utilize Natural Language Processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms to understand user queries, provide relevant responses, and perform specific tasks. Unlike traditional chatbots, which often rely on scripted responses, AI chatbots learn from interactions, continuously improving their performance over time.
Market Demand
The demand for AI-powered chatbots is rapidly increasing as businesses seek to enhance customer service while reducing operational costs. According to a report by Statista, the global chatbot market is expected to reach $1.34 billion by 2024, growing at a significant rate due to the rising need for 24/7 customer support and instant responses. Companies across various sectors — such as e-commerce, healthcare, and finance — are adopting chatbots to improve user engagement and streamline operations.
Key Features
- 24/7 Availability: AI chatbots can provide round-the-clock support, addressing customer inquiries at any time, thus improving customer satisfaction.
- Personalized Interactions: By analyzing user data and previous interactions, chatbots can offer personalized recommendations and responses, enhancing the customer experience.
- Multi-Platform Integration: AI chatbots can be integrated across various platforms, including websites, mobile apps, and social media, allowing businesses to engage with customers wherever they are.
- Scalability: AI chatbots can handle thousands of queries simultaneously, making them ideal for businesses experiencing high volumes of customer interactions.
- Learning Capabilities: Leveraging machine learning, these chatbots can improve their responses and functionalities based on user feedback and data analysis, leading to better accuracy over time.
Potential Challenges
While the benefits of AI-powered chatbots are substantial, there are challenges that startups should consider:
- Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Achieving accurate understanding and interpretation of human language can be complex. Poorly designed chatbots may misinterpret queries, leading to frustration among users.
- User Experience Design: Developing an intuitive user interface that provides a seamless interaction experience is crucial. A poorly designed chatbot can deter users and negatively impact brand reputation.
- Data Security: Handling sensitive customer information requires robust security measures to protect against data breaches and ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR.
- Continuous Improvement: To maintain effectiveness, chatbots must be regularly updated and trained on new data to adapt to changing user needs and language trends.
Business Opportunities
For startups looking to enter the AI-powered chatbot space, several opportunities exist:
- Niche-Specific Solutions: Developing chatbots tailored to specific industries (e.g., healthcare, finance, education) can help address unique challenges and requirements.
- Integration Services: Offering integration services for businesses to incorporate chatbots into their existing systems and platforms can provide a competitive edge.
- Performance Analytics: Building analytics tools that measure chatbot performance, user engagement, and customer satisfaction can help businesses optimize their chatbot strategies.
- Voice-Activated Chatbots: With the rise of voice assistants, creating voice-activated chatbots for applications like customer support or virtual shopping assistants can tap into a growing market.
Overview
AI in HealthTech refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance healthcare delivery, improve patient outcomes, and streamline operations within healthcare systems. This includes a wide range of applications, such as diagnostics, patient monitoring, personalized medicine, and administrative tasks. By leveraging AI, healthcare providers can harness vast amounts of data to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to improved healthcare services.
Market Demand
The HealthTech industry is experiencing unprecedented growth, driven by the increasing adoption of technology in healthcare and the demand for more efficient and effective solutions. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global AI in healthcare market is projected to reach $45.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 44.9% from 2021. This surge is largely attributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the need for cost-effective healthcare solutions.
Key Features
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can analyze historical health data to predict patient outcomes, enabling early intervention and personalized treatment plans. For example, machine learning models can assess the risk of conditions like diabetes or heart disease based on patient data.
- Medical Imaging and Diagnostics: AI tools can enhance the accuracy of medical imaging analysis, helping radiologists detect anomalies such as tumors or fractures more quickly and accurately. Companies like Zebra Medical Vision use AI to analyze medical images and provide actionable insights to healthcare professionals.
- Telemedicine Support: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can facilitate telemedicine by triaging patient symptoms, scheduling appointments, and providing health information, making healthcare more accessible.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: AI can analyze genetic data and patient history to tailor treatment plans to individual patients, increasing the effectiveness of therapies. This is particularly valuable in oncology, where precision medicine is becoming the standard of care.
- Operational Efficiency: AI can automate administrative tasks, such as billing and appointment scheduling, reducing administrative burdens on healthcare staff and allowing them to focus more on patient care.
Potential Challenges
Despite the potential benefits, startups venturing into the HealthTech space must navigate several challenges:
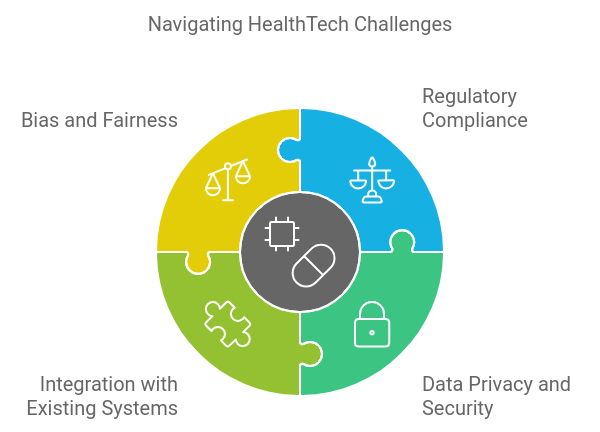
- Regulatory Compliance: The healthcare industry is heavily regulated, and startups must ensure their AI solutions comply with relevant regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States. This may include thorough testing and validation procedures.
- Data Privacy and Security: Handling sensitive patient information necessitates robust data security measures to prevent breaches and maintain patient trust. Startups must implement strict data governance practices.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Many healthcare providers use legacy systems, making it challenging to integrate new AI solutions. Startups need to develop systems that can seamlessly work with existing infrastructure.
- Bias and Fairness: AI algorithms trained on biased data can perpetuate disparities in healthcare. Startups must focus on creating fair and unbiased AI models that consider diverse patient populations.
Business Opportunities
For startups interested in AI in HealthTech, several promising opportunities exist:
- AI-Driven Diagnostic Tools: Developing AI applications that assist in diagnostics can significantly enhance the speed and accuracy of disease detection, particularly in fields like radiology and pathology.
- Remote Patient Monitoring Solutions: Creating AI-enabled devices or applications that monitor patients’ vital signs in real-time can help healthcare providers respond promptly to deteriorating conditions.
- Healthcare Analytics Platforms: Startups can build platforms that aggregate and analyze health data from multiple sources, providing actionable insights for healthcare providers and improving decision-making processes.
- Mental Health Support Applications: AI chatbots and virtual therapy platforms can offer accessible mental health support, addressing the growing demand for mental health services.
- Drug Discovery and Development: Leveraging AI to analyze biological data can accelerate the drug discovery process, enabling more efficient development of new medications.
Overview
AI-driven market research refers to the use of artificial intelligence technologies to gather, analyze, and interpret data about consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive landscapes. This approach allows businesses to make informed strategic decisions based on real-time insights. By automating data collection and analysis processes, AI enables companies to adapt quickly to market changes and consumer preferences.
Market Demand
With the increasing volume of data generated every day, traditional market research methods are often insufficient to keep pace. According to a report by ResearchAndMarkets, the global AI in marketing market is expected to reach $40.09 billion by 2025, reflecting a growing demand for data-driven decision-making. Businesses are seeking innovative solutions to understand their customers better and stay ahead of the competition.
Key Features
- Data Analysis Automation: AI can process vast amounts of data in seconds, uncovering trends and patterns that would be time-consuming or impossible for human analysts to identify.
- Sentiment Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze social media, reviews, and other user-generated content to gauge public sentiment toward products or brands, helping businesses to adjust their marketing strategies accordingly.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can forecast market trends and consumer behaviors based on historical data, allowing companies to anticipate demand and make proactive business decisions.
- Customer Segmentation: Machine learning algorithms can identify and segment customers based on their behaviors and preferences, enabling targeted marketing campaigns.
- Real-Time Insights: AI tools provide real-time analytics, allowing businesses to respond quickly to changing market conditions or customer needs.
Potential Challenges
Startups in AI-driven market research must be aware of the following challenges:
- Data Quality: The effectiveness of AI models depends on the quality of the data used for training. Inaccurate insights can arise from unreliable data.
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting and analyzing consumer data raises privacy issues, and startups must comply with data protection regulations like GDPR.
- Integration with Existing Tools: Businesses often use various tools for market research; integrating AI solutions with existing systems can be complex.
Business Opportunities
Several business opportunities exist within AI-driven market research:
- Custom Analytics Solutions: Developing tailored analytics platforms that address specific industries or business needs can help companies optimize their market research efforts.
- Real-Time Dashboards: Creating intuitive dashboards that provide real-time insights and visualizations can empower businesses to make data-driven decisions quickly.
- Consumer Behavior Prediction Models: Startups can build AI models that predict consumer purchasing behaviors, assisting brands in their marketing strategies.
- Survey Automation Tools: AI-powered survey tools that analyze responses and provide insights can streamline the market research process for businesses.
Overview
AI-powered content creation involves the use of artificial intelligence technologies to generate written, visual, or audio content. AI tools can assist in producing high-quality content quickly and efficiently, helping businesses keep pace with the growing demand for digital content across various platforms.
Market Demand
The content marketing industry continues to expand, with businesses increasingly recognizing the need for engaging and informative content to attract and retain customers. A report by Content Marketing Institute highlights that 70% of marketers are actively investing in content marketing. AI-powered content creation tools help marketers streamline their efforts and produce content that resonates with their audiences.
Key Features
- Automated Writing: AI algorithms can generate articles, blogs, and social media posts, allowing businesses to maintain a consistent content output without the need for extensive human resources.
- SEO Optimization: AI tools can analyze search engine algorithms and optimize content for keywords, improving visibility and ranking on search engines.
- Content Personalization: AI can tailor content recommendations based on user behavior and preferences, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
- Multimedia Content Generation: AI technologies can also create images, videos, and audio content, providing businesses with a variety of content types to engage their audience.
- Content Analysis: AI can analyze content performance and audience engagement, helping businesses refine their content strategies for better results.
Potential Challenges
While AI-powered content creation offers numerous benefits, challenges exist:
- Quality Control: Ensuring that AI-generated content meets quality standards and aligns with brand voice can be difficult, necessitating human oversight.
- Originality and Creativity: AI tools may struggle to create truly original content, leading to concerns about redundancy or lack of creativity.
- Ethical Concerns: Issues regarding plagiarism and the authenticity of AI-generated content may arise, requiring startups to establish clear guidelines.
Business Opportunities
Startups can explore various opportunities within AI-powered content creation:
- Content Generation Platforms: Developing platforms that offer AI writing assistance or content generation can attract businesses looking to streamline their content creation process.
- SEO-Focused Tools: Creating AI tools that analyze and optimize content for search engines can help businesses improve their online presence.
- Multimedia Creation Services: Startups can provide services that utilize AI to create videos or graphics tailored to marketing campaigns.
- Content Performance Analytics: Building analytics tools that measure content effectiveness and audience engagement can help businesses refine their strategies.
Overview
AI in e-commerce involves the application of artificial intelligence technologies to enhance online shopping experiences, streamline operations, and improve customer engagement. From personalized product recommendations to chatbots for customer support, AI plays a crucial role in transforming the e-commerce landscape.
Market Demand
The e-commerce industry is booming, with consumers increasingly turning to online shopping. According to eMarketer, global e-commerce sales are expected to reach $6.39 trillion by 2024. To stay competitive, retailers are leveraging AI to create more engaging and efficient shopping experiences.
Key Features
- Personalized Recommendations: AI algorithms analyze customer data to provide tailored product suggestions, enhancing the shopping experience and increasing conversion rates.
- Chatbots for Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots can assist customers in real time, answering questions and resolving issues quickly, thereby improving customer satisfaction.
- Inventory Management: AI can optimize inventory levels by predicting demand patterns, helping businesses reduce overstock and stockouts.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI algorithms can adjust prices based on demand, competition, and other market factors, maximizing profitability.
- Fraud Detection: AI systems can analyze transaction patterns to identify and prevent fraudulent activities, safeguarding businesses and customers.
Potential Challenges
While the benefits of AI in e-commerce are clear, challenges remain:
- Data Privacy: Collecting and analyzing customer data raises privacy concerns, requiring compliance with regulations such as GDPR.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many e-commerce platforms use outdated systems, making it difficult to implement new AI technologies.
- User Acceptance: Some customers may be resistant to AI-driven experiences, preferring human interaction over automated solutions.
Business Opportunities
Startups can explore various opportunities in AI for e-commerce:
- Personalization Engines: Developing AI platforms that provide personalized shopping experiences can help retailers boost sales and customer loyalty.
- AI-Powered Chatbot Solutions: Offering customizable chatbot services can enable retailers to improve their customer service without significant investments.
- Inventory Optimization Tools: Startups can create AI solutions that help businesses manage their inventory more effectively, reducing costs and improving efficiency.
- Fraud Prevention Solutions: Building AI-driven fraud detection systems can provide valuable security to e-commerce businesses.
Overview
AI-based fraud detection involves the use of artificial intelligence technologies to identify and prevent fraudulent activities across various sectors, including finance, insurance, and e-commerce. By analyzing patterns and anomalies in data, AI systems can flag suspicious transactions and behaviors in real time.
Market Demand
The growing incidence of fraud, particularly in online transactions, has increased the demand for effective fraud detection solutions. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global fraud detection and prevention market is projected to reach $63.5 billion by 2023. Businesses are actively seeking AI-driven solutions to mitigate risks and protect their assets.
Key Features
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI systems can analyze transactions as they occur, allowing businesses to detect and respond to fraudulent activities immediately.
- Anomaly Detection: Machine learning algorithms can identify unusual patterns in transaction data that may indicate fraudulent behavior, even when the fraud is previously unknown.
- Risk Scoring: AI can assign risk scores to transactions based on various factors, enabling businesses to prioritize investigations on high-risk cases.
- Adaptive Learning: AI systems can continuously learn from new data, improving their ability to detect emerging fraud patterns and tactics.
- Integration Capabilities: AI fraud detection tools can be integrated into existing systems, providing seamless protection without disrupting business operations.
Potential Challenges
Startups in AI-based fraud detection should be aware of the following challenges:
- False Positives: AI systems may incorrectly flag legitimate transactions as fraudulent, leading to customer dissatisfaction and lost revenue.
- Data Privacy: Analyzing sensitive customer data raises privacy concerns, necessitating compliance with regulations such as GDPR.
- Complexity of Integration: Integrating AI fraud detection systems with existing financial infrastructures can be challenging and resource-intensive.
Business Opportunities
Several business opportunities exist within AI-based fraud detection:
- Custom Fraud Detection Solutions: Developing tailored fraud detection systems for specific industries (e.g., finance, e-commerce) can address unique challenges.
- Risk Assessment Platforms: Startups can create platforms that provide comprehensive risk assessments for businesses, helping them make informed decisions.
- User Behavior Analytics: Offering solutions that analyze user behavior to identify potential fraud can enhance security measures for businesses.
- Consulting Services: Providing expert consulting on implementing AI fraud detection solutions can help businesses navigate the complexities of adoption.
Overview
AI for personal finance management involves leveraging artificial intelligence technologies to help individuals manage their finances more effectively. From budgeting tools to investment advisors, AI applications can analyze financial data and provide personalized recommendations to improve financial health.
Market Demand
As consumers become increasingly aware of the importance of financial literacy and management, the demand for personal finance management solutions is on the rise. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global personal finance software market is expected to reach $1.57 billion by 2025. AI tools can simplify financial management, making it more accessible to a broader audience.
Key Features
- Budgeting Assistance: AI applications can analyze spending habits and suggest budgets, helping users to save money and manage expenses more effectively.
- Expense Tracking: AI tools can automatically categorize expenses, providing users with insights into their spending patterns and areas where they can cut costs.
- Investment Recommendations: AI algorithms can analyze market trends and user risk tolerance to provide personalized investment strategies.
- Financial Goal Setting: AI can help users set and track financial goals, offering suggestions to achieve those goals more efficiently.
- Credit Score Monitoring: AI tools can monitor users’ credit scores and provide recommendations for improving credit health.
Potential Challenges
Startups in personal finance management using AI should consider the following challenges:
- Data Security: Handling sensitive financial information necessitates robust security measures to protect against breaches.
- User Trust: Building trust with users is crucial, as they must feel comfortable sharing their financial data with AI applications.
- Compliance: Startups must ensure compliance with financial regulations and data protection laws to avoid legal issues.
Business Opportunities
Several business opportunities exist in the realm of AI for personal finance management:
- AI-Driven Budgeting Apps: Developing user-friendly budgeting applications that leverage AI to provide personalized insights can attract consumers looking for financial management solutions.
- Investment Platforms: Startups can create platforms that offer AI-powered investment advice, catering to novice and experienced investors alike.
- Expense Management Tools for Businesses: Offering AI solutions that help businesses manage employee expenses and budgets can improve operational efficiency.
- Financial Education Resources: Building platforms that provide financial education and tools to help users understand personal finance better can address a growing need.
Overview
AI-enhanced cybersecurity involves the application of artificial intelligence technologies to protect systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and data analytics, AI can detect and respond to security incidents in real-time, improving overall cybersecurity posture.
Market Demand
As cyber threats become more sophisticated and frequent, the demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions is increasing. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybersecurity spending is projected to exceed $1 trillion from 2017 to 2021. Organizations are increasingly turning to AI to enhance their cybersecurity measures and safeguard sensitive information.
Key Features
- Threat Detection and Response: AI systems can analyze network traffic and user behavior to identify and respond to potential threats in real-time, minimizing response times.
- Anomaly Detection: Machine learning algorithms can identify unusual patterns in data that may indicate a security breach, allowing for rapid investigation and mitigation.
- Automated Incident Response: AI can automate incident response processes, enabling organizations to react quickly to threats without human intervention.
- Vulnerability Management: AI tools can assess system vulnerabilities and provide recommendations for remediation, helping organizations strengthen their security defenses.
- User Behavior Analytics: By analyzing user behavior, AI can detect insider threats and unauthorized access attempts, enhancing overall security measures.
Potential Challenges
Startups in AI-enhanced cybersecurity should be aware of the following challenges:
- Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and AI systems must continuously learn and adapt to new attack vectors.
- False Positives: AI systems may generate false alarms, leading to alert fatigue and potential oversight of genuine threats.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating AI cybersecurity solutions with existing security infrastructures can be complex and resource-intensive.
Business Opportunities
Several business opportunities exist within AI-enhanced cybersecurity:
- Threat Intelligence Platforms: Developing AI-driven platforms that aggregate and analyze threat intelligence can help organizations stay informed about potential risks.
- Automated Security Solutions: Startups can offer automated solutions that streamline incident response processes, reducing the burden on security teams.
- Vulnerability Assessment Tools: Creating tools that leverage AI to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities can help organizations improve their security posture.
- Consulting Services: Providing expert consulting on implementing AI cybersecurity solutions can help businesses navigate the complexities of adoption.
Overview
AI in human resources (HR) refers to the application of artificial intelligence technologies to streamline HR processes, improve recruitment, and enhance employee engagement. By automating various HR tasks, AI enables organizations to focus more on strategic initiatives and employee development.
Market Demand
The HR tech market is rapidly evolving, with organizations increasingly adopting technology to improve their HR functions. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global HR technology market is expected to reach $30.01 billion by 2025. AI-driven solutions are becoming essential for companies looking to enhance their HR capabilities and drive better employee outcomes.
Key Features
- Automated Recruitment: AI tools can automate the recruitment process by screening resumes, assessing candidate fit, and scheduling interviews, reducing time and effort for HR teams.
- Employee Onboarding: AI can streamline the onboarding process by providing new hires with personalized training plans and resources, ensuring a smoother transition.
- Performance Management: AI systems can analyze employee performance data, providing insights into strengths, weaknesses, and areas for development.
- Employee Engagement Tools: AI can facilitate employee engagement surveys and feedback mechanisms, helping organizations gather insights and improve workplace culture.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze employee data to predict turnover risks, allowing HR teams to proactively address issues and retain talent.
Potential Challenges
Startups in AI for HR must consider the following challenges:
- Bias in Algorithms: AI systems can perpetuate biases present in historical data, leading to unfair hiring practices. Ensuring fairness and diversity in AI algorithms is crucial.
- Data Privacy: Handling sensitive employee data requires robust security measures and compliance with regulations like GDPR.
- User Acceptance: Employees may be resistant to AI-driven processes, preferring human interaction in HR functions.
Business Opportunities
Several business opportunities exist within AI in HR:
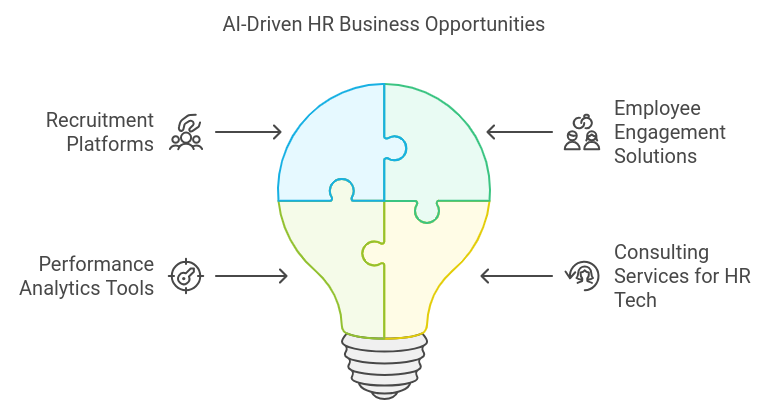
- Recruitment Platforms: Developing AI-driven recruitment platforms that streamline the hiring process can attract companies looking to enhance their talent acquisition efforts.
- Employee Engagement Solutions: Startups can create platforms that use AI to gather employee feedback and improve workplace culture.
- Performance Analytics Tools: Building tools that analyze employee performance data and provide actionable insights can help organizations optimize talent management strategies.
- Consulting Services for HR Tech: Offering consulting services to help organizations implement AI-driven HR solutions can provide valuable support in navigating the evolving landscape.
Overview
AI for supply chain management involves leveraging artificial intelligence technologies to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of supply chain operations. From demand forecasting to inventory management, AI can optimize various aspects of the supply chain, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
Market Demand
As globalization and e-commerce continue to grow, the demand for efficient supply chain management solutions is increasing. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global AI in supply chain market is expected to reach $10.1 billion by 2025. Companies are adopting AI technologies to enhance visibility, streamline processes, and respond more effectively to market changes.
Key Features
- Demand Forecasting: AI algorithms can analyze historical sales data and market trends to predict future demand, enabling businesses to optimize inventory levels.
- Inventory Optimization: AI can help organizations manage inventory more effectively by analyzing stock levels, lead times, and demand patterns.
- Logistics Optimization: AI can optimize transportation routes and delivery schedules, reducing costs and improving delivery times.
- Supplier Relationship Management: AI tools can analyze supplier performance data, helping businesses make informed decisions about partnerships and sourcing.
- Risk Management: AI can identify potential risks in the supply chain, allowing organizations to develop contingency plans and mitigate disruptions.
Potential Challenges
Startups in AI for supply chain management should be aware of the following challenges:
- Data Integration: Integrating AI solutions with existing supply chain systems can be complex and require significant resources.
- Data Quality: The effectiveness of AI algorithms depends on the quality of the data used for training. Poor data can lead to inaccurate forecasts and decisions.
- Change Management: Employees may resist adopting new AI-driven processes, necessitating effective change management strategies.
Business Opportunities
Several business opportunities exist in AI for supply chain management:
- AI-Powered Forecasting Tools: Developing tools that leverage AI for demand forecasting can help businesses optimize inventory and reduce costs.
- Logistics Optimization Platforms: Startups can create platforms that use AI to enhance logistics and transportation processes.
- Supplier Performance Analytics: Building solutions that analyze supplier data to improve decision-making can provide valuable insights for businesses.
- Consulting Services for Supply Chain Optimization: Offering consulting services to help organizations implement AI-driven supply chain solutions can address a growing need in the market.
In the rapidly evolving technological landscape, artificial intelligence (AI) offers immense opportunities for startups across various sectors. From improving customer experiences with AI-powered chatbots to transforming market research through data-driven insights, the potential applications of AI are vast and diverse. As more businesses recognize the importance of leveraging AI, startups that prioritize innovative solutions can establish a competitive edge. Understanding market demands and consumer needs while addressing challenges like data privacy and integration complexities is crucial for success. By harnessing the unique capabilities of AI, startups can develop value-added services that drive growth and create a more efficient business ecosystem.
As AI continues to integrate into various industries, it opens up new avenues for innovation and entrepreneurship. Startups that remain agile and adapt to changing market conditions will be well-positioned for long-term success. Embracing AI business ideas empowers businesses to optimize operations and cultivates a culture of innovation, leading to groundbreaking advancements and improved customer satisfaction. The exploration of top AI business ideas — from AI-driven market research to enhanced cybersecurity — highlights the vast potential that AI holds for startups. Entrepreneurs who venture into these domains will play a vital role in shaping the future of their industries, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of consumers and businesses alike.
What Are the Top 10 AI Business Ideas for Startups? was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
