Revolutionizing Interoperability: Across Protocol’s Intent-Based Solution for the EVM Landscape

Note -: This post is an entry for the BridgeAcrossWithACX contest in the Publish0x Platform
Intent-Based Interoperability for the EVM Landscape powered by Across ProtocolAcross Protocol stands out from other interoperability protocols in the Web3 ecosystem as the first intent-based interoperability solution. It is designed to enable seamless connectivity across the entire Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) landscape through its intent-powered interoperability operations.
Across’s products like Across Bridge and Across+, facilitate fast, low-cost, efficient, and secure interoperability between Layer 1 (L1) Ethereum, EVM Layer 2 (L2) networks, and between supported L2 solutions.
This interoperability is secure as well, as it is not brought about by trusting traditional 3rd party bridge protocols that compel users to trust a 3rd party in the safekeeping of their locked assets.
Across offers a simple interoperability solution compared to other complex alternatives, which can be costly for developers and time-consuming to implement due to the need for building extensive infrastructure.
 Cross-Chain Transactions expressed as Cross-chain Intent Order Execution Instructions
Cross-Chain Transactions expressed as Cross-chain Intent Order Execution InstructionsLet’s understand what Across Protocol’s intent-based interoperability means!
In Across, a user’s cross-chain transaction is treated as an intent order, which specifies the user’s desired outcome that needs to occur on the destination chain.
This approach contrasts with typical transactions in other protocols, which follow a lengthy series of execution paths and verification processes.
The intent order can be viewed as a cross-chain limit order, integrated with an action execution call.
Across Protocol has established an effective system that enables the efficient execution of users’ intent orders in a cost-effective and timely manner, allowing cross-chain transactions to be completed in under a minute.
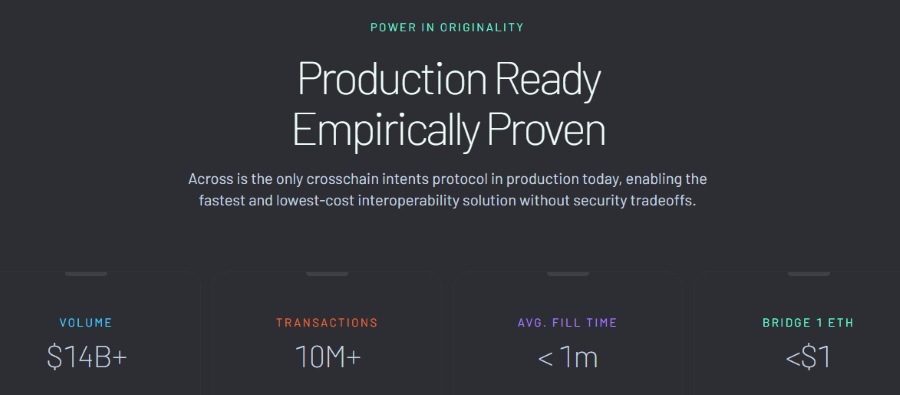 Users’ Cross-Chain Intent Orders Are Executed Instantly by Across’s Network of Relayers
Users’ Cross-Chain Intent Orders Are Executed Instantly by Across’s Network of Relayers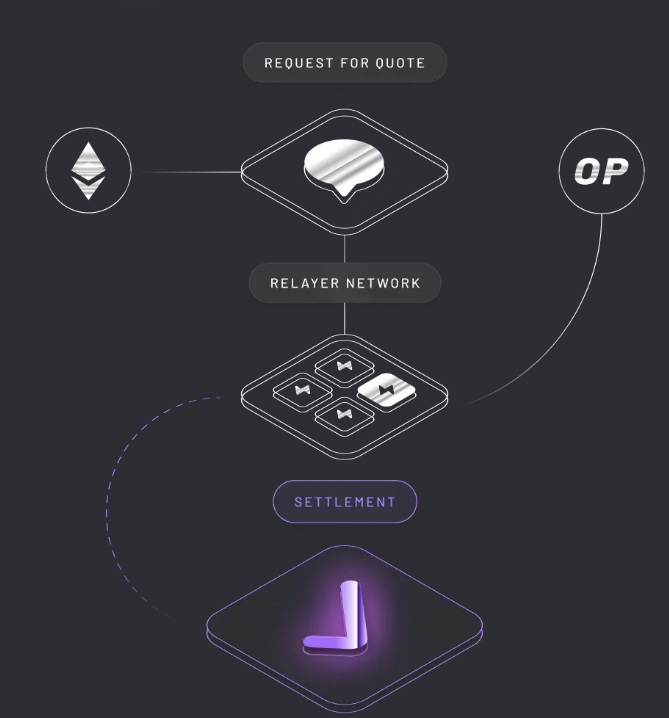
A user’s intent order is executed by a Relayer who is a part of Across’s decentralized Network of Relayers who compete with each other by quoting their fees.
The Relayer carries out the user’s intent order by transferring the corresponding output assets to the specified destination chain and address as outlined in the intent order.
The liquidity needed for the Relayer’s transaction is sourced from Across Network’s Liquidity Providers (LPs) for a fee.
For example, if a user wants to transfer USDC tokens from Polygon to Base or any other Layer 2 network, this request becomes an intent order. A Relayer processes this intent order for a quoted fee.
The Relayer simply transfers the USDC tokens to the specified address on Base as per the instructions in the intent order.
Across’s LPs promptly supply the USDC tokens to the Relayer for a fee, enabling the Relayer to execute the transfer according to the user’s intent order.
Subsequently, Across Protocol’s settlement layer, secured by UMA’s Decentralized Oracle, verifies these transactions and releases the funds to the Relayer accordingly.
Later, Across Protocol’s Settlement Layer, secured by Uma’s Decentralized Oracle, would verify these transactions and release users’ funds that are escrowed by the protocol when the user places his intent order to repay the relayer accordingly.
The standardized format for cross-chain intent orders in Across is ERC-7683Across’s intent design architecture and intent lifestyle process would be explained in detail but what can be understood so far is that Across has an established efficient system to ensure that users’ cross-chain transactions (expressed as cross-chain intents) get processed instantly as Relayers just do the needed transfers in the destination chain.
All users’ cross-chain transactions from Ethereum L1 and supported L2 Networks in Across will be converted to intent orders that are processed in a similar manner.
These intent orders follow a standardized intent order flow format, ERC-7683. This standardization ensures that all cross-chain transaction orders originating from various L2 Networks and Ethereum L1 are recognized by the Across Network, enabling efficient intent-based interoperability operations.
Across Protocol’s interoperability products — Across Bridge and Across+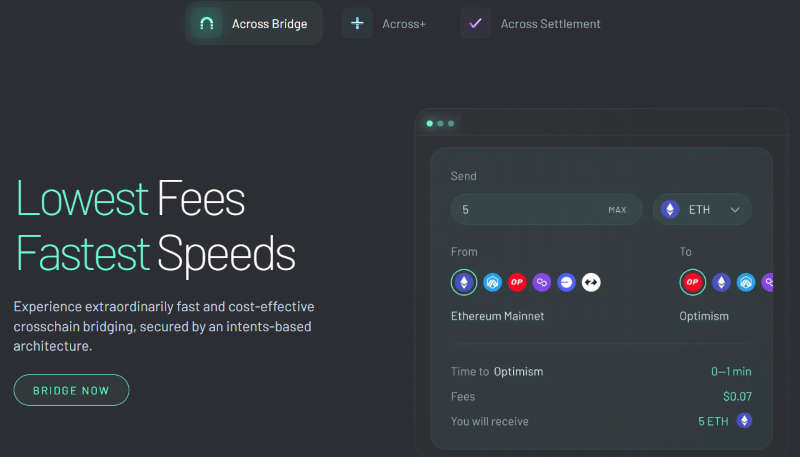
Across Protocol’s interoperability solutions establish efficient cross-chain connectivity within EVM ecosystem enabling quick and low-cost transactions between various L2 Networks within themselves and with L1 Ethereum. This interoperability is powered by interoperability operations brought about leveraging Across Protocol’s intent-based architecture.
Across Bridge facilities token value transfers between various L2 Networks and L1 Ethereum.
Across+ goes beyond this, with its cross-chain hooks feature triggering additional functionality of executing a protocol action like token swaps in the destination chain, apart from bringing capital from the source chain.
Any EVM L2 protocol can establish interoperability with the EVM ecosystem by integrating Across+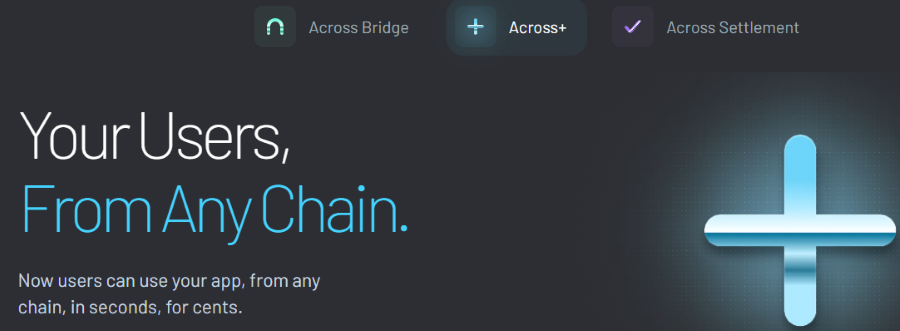
Integrating Across Bridge and Across+ into dapps is easy for developers as it does not require any smart contract work.
Dapp protocols that have integrated Across+ benefit because users can easily use these dapps bringing their assets residing in another L2 Network address.
The Dapp UX and user experience are improved as users don’t feel they are engaged in a complex bridging transaction. Cross-chain transactions, including cross-chain swaps, occur instantly and seamlessly.
Liquidity from dapps on other L2 Networks supported by Across+ can be accessed by any dapp that integrates Across+.
 Across provides advanced interoperability solutions like cross-chain swaps
Across provides advanced interoperability solutions like cross-chain swapsAcross Protocol’s intent-powered interoperability solutions enable cross-chain value transfers within the EVM landscape. This includes transactions between Layer 1 (L1) Ethereum, Layer 2 (L2) networks, and across different L2 networks. Additionally, these solutions facilitate cross-chain swaps among these various networks within the EVM ecosystem.
Advanced interoperability operations can be implemented using Across Protocol’s intent-based interoperability solutions.
For instance, a user intent-based order that details asset x in Chain A to be swapped for asset y in Chain B and then execute another protocol
action in Chain B is possible using Across’s interoperability solutions.
EVM Networks that have Across+ integrated to power interoperability between them
Across powered protocol — Straddl facilitating seamless cross-chain swaps between different EVM Networks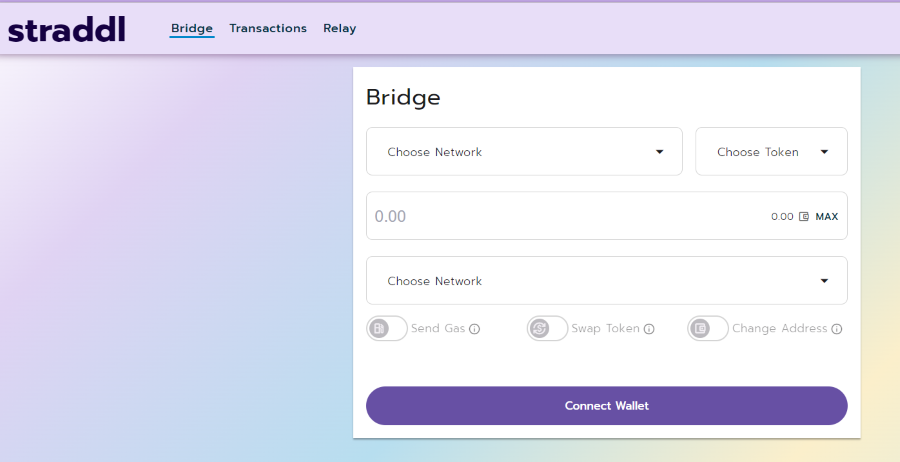
Straddl powered by Across Protocol facilitates seamless cross-chain swaps among EVM L2 Networks and between EVM L2 Networks and Ethereum Mainnet.
Check Straddl out here — https://straddl.io
Unifying the EVM landscape powering Networks with Across’s intents-based interoperabilityAcross Protocol’s intent-based interoperability solutions integrate the EVM ecosystem, allowing developers to host their dapp protocols on one EVM L2 Network while making them accessible to users of dapp protocols residing on other EVM L2 Network chains.
This connectivity unifies the otherwise siloed EVM ecosystem, which suffers from fragmented liquidity. Accessing liquidity across different EVM L2 Networks can be challenging without the interoperability solutions provided by Across Protocol.
Now, developers don’t need to deploy their dapps in every EVM L2 Network to catch users active in those Networks throughout the EVM ecosystem.
Users can interact with any dapp protocol within the EVM ecosystem and transfer assets from dapps on one L2 Network to dapps on another EVM L2 Network.
Additionally, users can conduct cross-chain swaps, exchanging one asset in their dapp for a different asset in a dapp located on another EVM L2 Network.
There is no longer a need for users to perform multiple transactions to move their assets from one EVM L2 chain to another and then execute a swap. All these actions can be combined, completely eliminating the complexity of bridging for users.
Understanding Across’s Intent-based architecture that powers the Protocol’s interoperability operations!Now, let’s understand Across’s Intent- based architecture that powers the protocol’s seamless interoperability operations within EVM landscape between L1 Ethereum and EVM L2 Networks.
Here is the framework. This is Across’s Intent-based design architecture powering the Protocol’s intent-based interoperability operations -
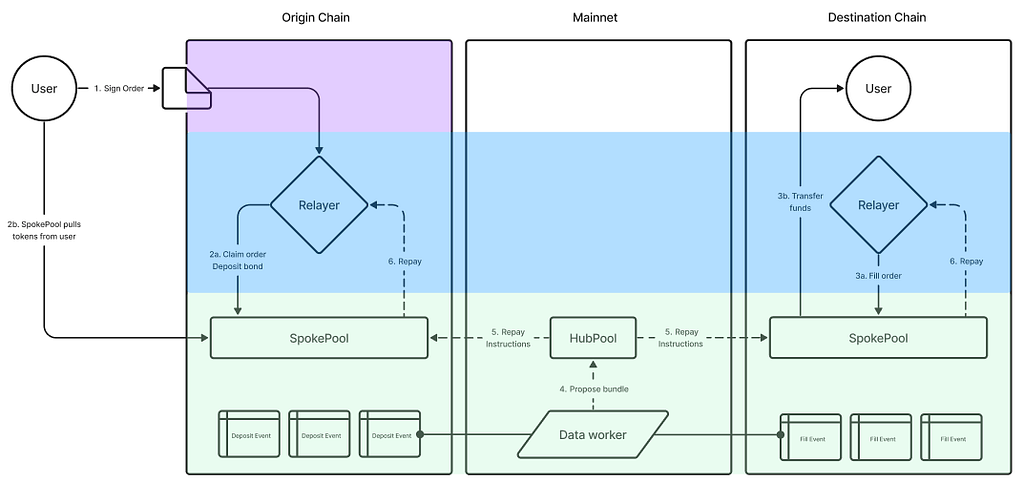
Creation of User’s cross-chain intent order!
User’s cross-chain intent order is generated.
In this first step, user requests a quote from Across Protocol’s decentralized Network of 3rd Party Relayers. Relayers compete with each other providing their quotes, that’s the price they charge to fill up user’s cross-chain intent order.
User accepts the service of the relayer whose quote is found to be most satisfactory. User does this by signing the relayer’s sent price quotation.
Once this is done, user’s intent order is activated and brought on chain.
User’s funds for filling his placed intent order is escrowed into the Spokepool Smart Contract in the Source Chain.
These user funds is the input amount that needs to be refunded to retailers after they fill up the user’s cross-chain intent order.
This amount would be released to relayers after Across’s Settlement Layer secured by UMA’s Decentralised Oracle verifies that the relayer has correctly filled up the user’s cross-chain intent order.
Data that’s embedded in a User’s Cross-Chain Intent Order as instructions to be executed
Users from any EVM L2 chain can generate an intent order. However, it should be translated into a format which is understood by Spokepool. The accepted format for user’s cross-chain intent order is ERC-7683, so all users cross-chain intent order adheres to ERC-7683 standard.
When user’s funds is deposited into the Spokepool Smart Contract a Deposit Event is emitted, which needs to be filled by the Relayer who has agreed to fill this deposit Event.
A User’s intent order contains instructions which needs to be implemented accordingly. It has details of the user’s input token, user’s input amount, the Network and address in which the Relayer should dispatch output token along with the output amount they need to send. The time frame within which this intent order is to be fulfilled is also mentioned.
Additionally, a custom message may be embedded if a protocol action has to be executed by the destination chain’s smart contract (like cross-chain swap instruction).
The Relayer instantly sends output funds to the user…
Now, Relayer’s part activates. The Relayer deposits output token and output amount in destination chain’s Spokepool Contract. Relayer can acquire liquidity to fill up the user’s intent order from passive Liquidity Providers in Across Hub.
Relayer would provide details on which chain user’s escrowed funds should be dispatched to him.
The output amount that Relayers agree to fill user’s intent order is computed considering the fees that relayer has to pay to LPs, the fee relayers incur in form of gas fees while dispatching funds to the destination chain, and the Relayer’s fee for performing the task.
Once Relayer fills up the user’s intent order by sending funds to the destination chain’s Spokepool contract, a FillEvent is emitted.
Users, immediately receive funds when the destination chain’s Spokepool contract receives funds.
Funds released to relayers after verification of their intent order fill transactions
User funds that are escrowed now need to be released to the Relayer, which would be released only after the relayer’s FillEvent is verified to be valid by UMA’s Decentralised Oracle.
Dataworkers in Across’s mainnet do this task of verifying Relayer’s FillEvent Transaction.
They aggregate all valid intent Order fill events and match it with a Deposit Event. This becomes a relayer repayment bundle which the Data Worker proposes to be optimistically verified.
Data Workers need to bond Across Bond Token(ABT) when proposing a bundle for verification. This bundle along with ABT Bond is locked in Across’s Hub Pool Contract.
This repayment bundle is opened for intense verification for a 60 minute time frame. This is the challenge period where disputes can be raised regarding the validity of transactions posted to be optimistically verified. The disputer also posts ABT Bond, when raising a dispute.
If no disputes occur, the Data Worker executes the repayment bundle, and the Hub Contract dispatches funds to Relayers according to the details supplied by Relayers on which chain they want to receive funds.
.If Data Workers proposed bundle was found to have included intent order fill transactions that are not valid, the Data Workers ABT Bond is forfeited and awarded to the disputer, who found this error and raised the dispute!
This is a outline of how Across Protocol’s intend-based system functions, for more indept details please read Across Protocols documentation on this here — https://docs.across.to/concepts/intents-architecture-in-across
Users cross-cross outcomes happen instantly as relays bear the delay related to verification of transaction validity!
Across Protocol intents powered interoperability operations ensure users cross-chain transactions within the EVM ecosystem happen quicky.
Verification of transactions are done, but the delay for this is borne by 3rd party Relayers who are compensated for this, with fees paid to them by users for their services.
Relayers receive funds in EVM L2 chain of their choice as well which is convenient for them.
Content and images Sources -
Across Documentation -: — https://docs.across.to
Across Protocol Website -: https://across.to/
My article can also be found in these platforms I post my content on-:
Hive — https://ecency.com/hive-150329/@mintymilecan
Publish0x — https://www.publish0x.com/@greenchic
Medium — https://medium.com/@kikctikcy
t2World — https://app.t2.world/
Revolutionizing Interoperability: Across Protocol’s Intent-Based Solution for the EVM Landscape was originally published in Coinmonks on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
